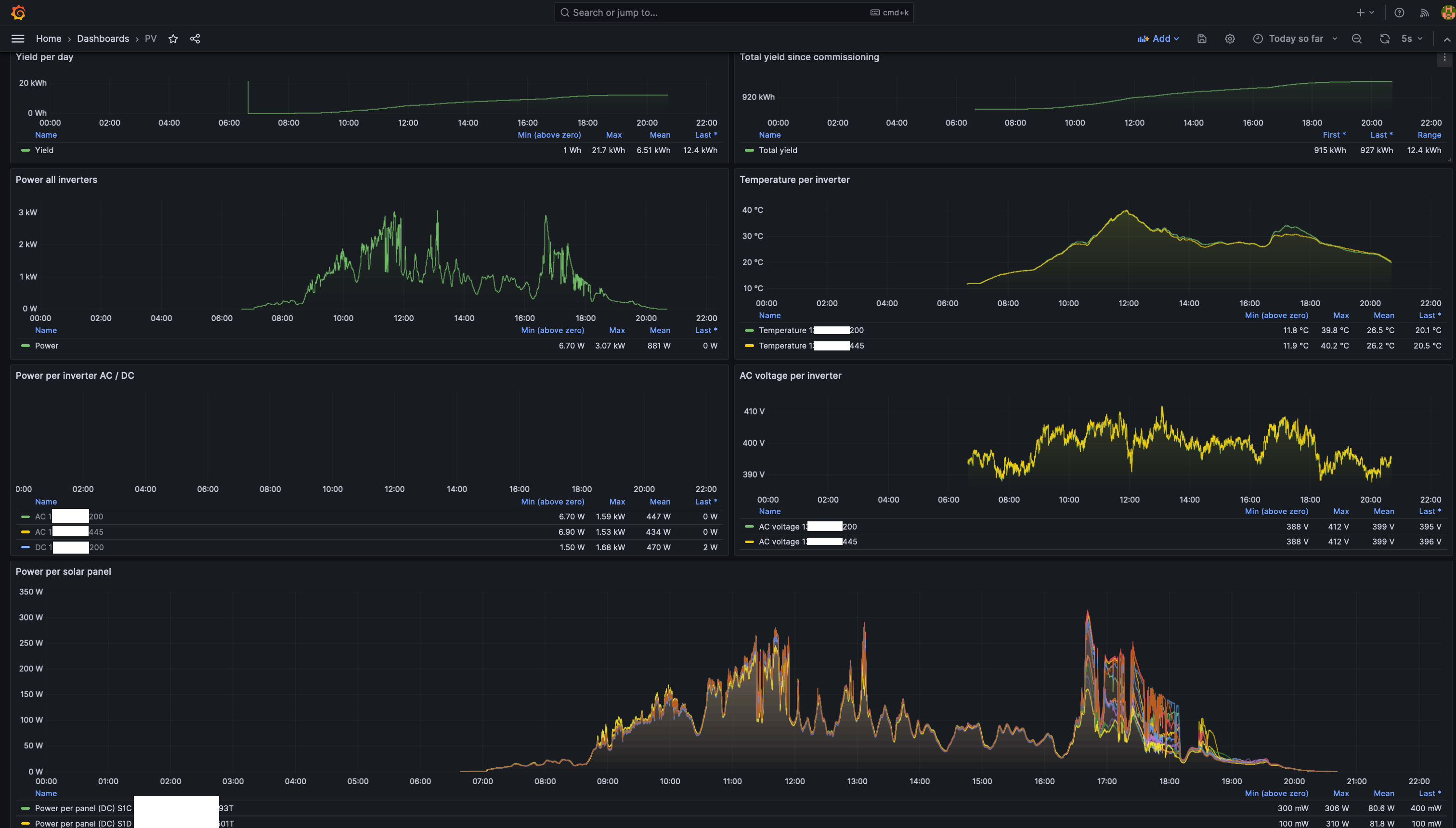
Included in OpenDTU Logger are a number of Grafana dashboards, which can be used to provide useful visualisations and insights. The image below shows the PV dashboard of a given day in dark mode. Light mode is also supported. Hovering over the graphs will result in a tooltip, providing exact the values recorded at a given time.
The `docker` folder in this [repository](https://git.hollander.online/energy/opendtu-logger) contains example Docker compose files. The `compose.with-database-grafana.yml` file contains a full setup suitable for a standalone deployment. The other compose files are aimed at integration into existing environments.
- In `DB_URL` alter the `password` field. Set the same value in. `PG_PASSWORD`
Deploy the Docker containers by running the following command from the `docker` folder.
```sh
docker compose -f compose.with-database-grafana.yml up
```
Docker should now start downloading the required containers and bring up OpenDTU Logger, TimescaleDB and Grafana. If everything seems ok, press `CTRL + C` to stop the containers. Next, execute
```sh
docker compose -f compose.with-database-grafana.yml up -d
The `-d` flag ensures that the containers are started in the background, so you can safely close your terminal window. If desired, containers running in the background can be stopped by running compose again with the `down` command.
The initial login username and password are `admin:admin`. After the initial login, Grafana will request you to change the password to something more secure.
##### Configuring the OpenDTU Logger data source
After logging in, go to `Connections` -> `Data sources` -> `Add new data source`.
- Under `SQL` select `PostgreSQL`.
- Change the following fields
-`Host URL`: `timescaledb:5432`
-`Database name`: `opendtu_logger`
-`Username`: `postgres`
-`Password`: The password you set in the `.env.` file in the previous step.
-`TLS/SSL Mode`: `disable`
-`TimescaleDB`: set the slider to `enable`
- Click `Save and test`
- You should get a green box with a `Database Connection OK` message.
##### Adding the OpenDTU Logger dashboards
Now that the data source has been configured, we can add our dashboards.
- Go to `Dashboards` -> `New` -> `Import`.
- Upload `PV.json` from the `grafana` folder in this [repository](https://git.hollander.online/energy/opendtu-logger)
- After uploading, Grafana requests you to configure a data source. Select the data source configured in the previous step. Click `Import`. The dashboard should now be ready.
- If you want more dashboards, import the other dashboards from the `grafana` folder as well, or create your own.
The OpenDTU logger logs to a PostgreSQL database and optionally supports TimescaleDB. Create a separate database and user using the following commands.
Optional: enable the TimescaleDB extension. To make use of TimescaleDB, follow the steps outlined in [their documentation](https://docs.timescale.com/self-hosted/latest/install/installation-linux/). Then, enable TimescaleDB support for the `opendtu_logger` database by executing the following commands
-`REMOTE_URL`is used to specify the IP address or hostname OpenDTU is running on. E.g.: `192.168.1.6` or `opendtu.internal`
-`DB_URL` specifies the credentials required to connect to the PostgreSQL database. All [connection parameters documented by golang's `lib/pq` package](https://pkg.go.dev/github.com/lib/pq#hdr-Connection_String_Parameters) can be used.
-`TIMESCALEDB_ENABLED` should be set to `true` or `false`.
-`TZ` is used to ensure data is recorded with the right timestamp. Choose the timezone valid for your location from [this Wikipedia page](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_tz_database_time_zones).
The `grafana` folder contains example dashboards which can be imported into existing Grafana installs, or into the provided Docker Compose with Grafana setup.
- The logger will currently log every event posted by OpenDTU to the websocket. Checks still need to be added to determine the uniqueness of an event. For more information, see also [this OpenDTU Github issue](https://github.com/tbnobody/OpenDTU/issues/1800).
- Upon restart of the OpenDTU, the OpenDTU Logger binary will need to be restarted as well. When using the provided `compose.yml` files with Docker, or using the `systemd` service file when using the binary, this will happen automatically.
If you'd like to provide feedback about this project, or in case you'd like to ask questions, please refer to [this page](https://pieterhollander.nl/author/pieter-hollander/) for contact information (e-mail, Github or LinkedIn), or use the [contact form](https://pieterhollander.nl/#contact) on my website. You can also respond by placing your remarks in [this discussion on Github](https://github.com/tbnobody/OpenDTU/discussions/1842).